Ans.
The flow of flow of free electron is called electricity . Electricity or electrical energy is a sort of energy which can be experienced in its application like electric bulb, heater, television, motor etc.
State Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
Ans.
Faraday gave the following two laws…………
FIRST LAW :- It states whenever the magnetic flux linked with a coil or circuit changes, an e.m.f. is always induced in it. This e.m.f. is exist in the circuit or coil as long as the changes in magnetic flux continues.
OR
It states, whenever a conductor cuts magnetic flux, an e.m.f. is induced in that conductor.
SECOND LAW :- It states, the magnitude of induced e.m.f. is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linked with the circuit or coil.
We may also say that the magnitude of induced e.m.f. is equal to the rate of change of flux-linkages.Explain the term induced emf?
Ans :- Whenever magnetic flux linked with the coil changes, an emf is always induced in it . This change in magnetic flux can be brought in the following two ways……………..
(a) If the conductor is moved in a stationary magnetic field in such a way that the magnetic flux linked with it changes in magnitude. Then, the emf induced in this way is called dynamically induced emf.
(b) If the conductor is stationary and the magnetic field is moving or changing. The emf induced in this way is called statically induced emf. It is so called because the emf induced in the conductor which is stationary. A statically induced emf is further sub-divided into……..
(i) Self-induced emf & (ii) Mutually-induced emf
How a force experienced on a current carrying conductor laying in a uniform magnetic field . Explain ?
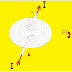
Ans. When a current carrying conductor is placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, it is found that the conductor experienced a force which acts in a direction perpendicular both to the direction of current & the field .
Consider a straight conductor placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of flux density B wb/m2 (produced by two magnet A & B) .
If the length of the conductor is L meter laying within this field & it carries a current of I ampere, then the force F experienced by the conductor is given by ;
F = BIL Newton
The direction of this force may be easily found by Fleming left-hand rule . It is explain as…..
If we hold out our left hand with fore ( first ) figure, second figure & the thumb at right angles to one another . Then according to Fleming left-hand rule, if the first fingure represents the direction of magnetic field & second figure points towards the direction of current, then thumb gives the direction of the motion of the conductor .
If the direction of any two of F,B & I are known then the direction of the third can be found by this rule .
What is reluctance ?
Ans. It is the name given to that property of a substance/material which opposes the creation of magnetic flux in it . In fact, it measures the opposition offered to the passage of magnetic flux through a material . Its unit is AT/Wb .
Reluctance in a magnetic material corresponds to resistance in an electric circuit .
What is magnetism ?
Ans :- Magnetism is the property of a certain materials of attracting small iron pieces towards them .
What is a magnet ?
Ans :- A magnet is a piece of iron or any other magnetic material which can attract small iron pieces towards it .