What is magnetic circuit ?
Ans :- The closed path followed by magnetic flux is called magnetic circuit .
In a magnetic circuit, the magnetic flux leaves the n-pole, passes through the entire circuit and returns to the starting point. A magnetic circuit usually consists of materials having high permeability e.g., iron, soft steel etc . It is because these materials offer very small opposition to the flow of magnetic flux. Consider a coil of N turns wound on an iron core as shown in the figure (10). When current I is passed through the coil, magnetic flux is set up in the core. The magnetic flux flows the closed path ABCD. The amount of flux set up in the core depends upon current (I) and number of turns (N). The product of NI is called magneto-motive force ( mmf ) . That is ………. MMF = NI ampere-turns
The opposition ( reluctance ) that magnetic circuit offers to the magnetic flux, depends upon length of magnetic circuit, area of cross-section of the circuit and the nature of the material that makes up the magnetic circuit . Figure (10)…………………………….
How direction of induced emf and hence current in a conductor can be found ?
Ans :- The direction of induced emf & hence current in a conductor or a coil can be determined by one of the following methods :-----
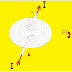
(A) Fleming’s Right-hand rule :- This rule is particularly suitable to find the direction of induced current , the direction of flux and the motion of the conductor. It may be stated as under…………..
If we hold out our right hand with first figure ( fore figure ), second figure ( middle figure ) & thumb so that they are at right angles to one another. Then according to this rule, if the fore figure represents towards the direction of magnetic field and thumb represent the direction of motion of the conductor, then middle figure will point in the direction of induced current.
Consider a conductor AB moving upwards at right angles to a uniform magnetic field as shown in the above figure. Applying Fleming’s Right-hand rule it is clear that the direction of induced current is from B to A.
(B) Lenz law :- The direction of induced current may also be found by this law . This law states that electromagnetically induced current always flows in such a direction that the action of magnetic field set up by it tends to oppose the very cause which produces it.
What are the principal properties of a magnet ?
Ans :-
(i) A freely suspended magnet always rests in a north-south direction.
(ii) Like poles of two magnets repel and unlike poles attract each other.
(iii) Each magnet has two poles, one north-pole and other south-pole.
What is the molecular theory of magnetism ?
Ans :-
Every molecule of a substance behaves like a tiny magnet because of its spin motion. It has a north-pole and a south-pole. When these tiny magnets of a material are set in a definite linear order, the substance then starts to behave as a magnet.
What are the principal magnetic materials ?
Ans :-
Principal magnetic materials are iron, nickel, cobalt, steel etc.
What is a pole ?
Ans :-
A pole is the point in a magnet where the intensity of magnetic lines of force is maximum.
What is meant by magnetic lines of force ?
Ans :-
A magnetic lines of force is an imaginary closed curve which starts from north-pole of the magnet and it terminates at south-pole. The curve completes its path through the magnet from south-pole to north-pole.
What is magnetic-axis ?
Ans :-
The straight line passing through the two poles of a magnet is called magnetic axis.
What will happen if a magnet is broken into several pieces?
Ans :-
Each magnet piece will behave as an independent magnet.
What are the various shapes in which permanent magnets are usually made ?
Ans :-
Bar, horse-shoe, ring etc.